夏威夷豆 / 杏 仁 / 腰 果 / 核 桃 / 胡 桃 / 南瓜子 / 巴西豆 / 開心果 / 榛 果 / 松 子 /
胡桃,這種口感獨特、香脆可口的美味堅果,數百年來一直迷住了世界各地的人們。從成為美洲原住民部落的主要糧食來源,到成為各種烹飪創意中不可或缺的成分,胡桃擁有著豐富的歷史和文化意義。在本文中,我們將探索胡桃的世界,揭示其營養益處,深入了解其種植和生產過程,以及發現它在烹飪和烘焙中的多種應用。
什麼是胡桃?
胡桃是一種生長在胡桃樹上的堅果,其外殼堅硬,內含有核仁。這種堅果呈橢圓形,表面有著紋路和顏色的變化。胡桃的外殼通常需要剝離才能食用核仁。
胡桃的歷史意義
胡桃在世界各地的歷史上扮演了重要角色。早在公元前7000年,胡桃就被人們視為重要的食物來源。在古希臘和羅馬文化中,胡桃被視為財富和健康的象徵。它在中世紀的歐洲也非常受歡迎,被廣泛用於料理和藥用。
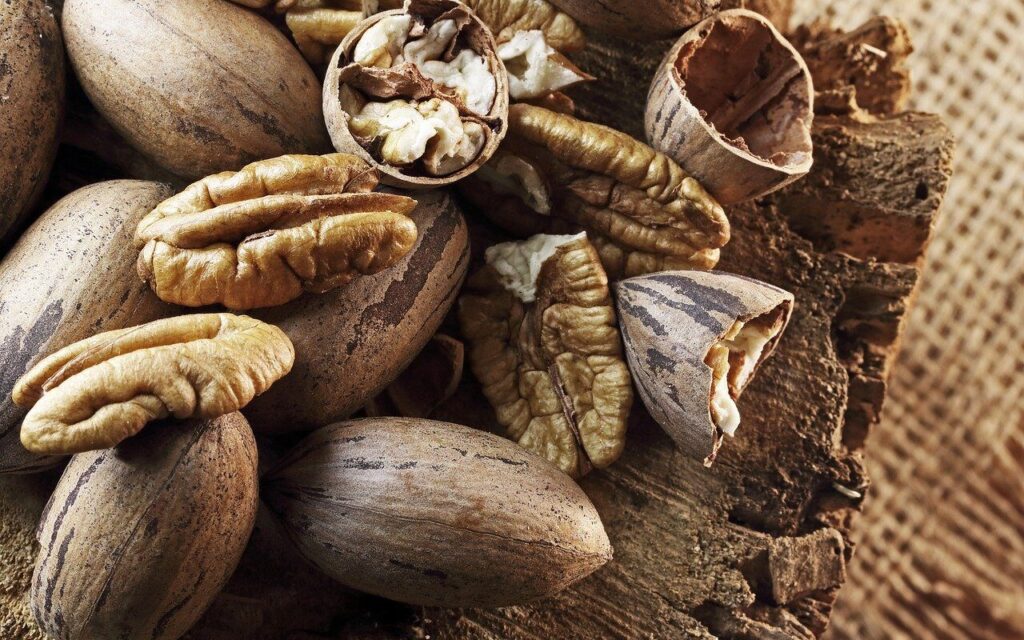

胡桃的種植和生產
4.1 胡桃樹
胡桃樹是生長胡桃的主要樹種。這種樹是中大型喬木,可以長到20到30英尺高。胡桃樹具有強大的生命力和耐寒性,可以生長在寒冷的氣候條件下。
4.2 生長條件
胡桃樹需要陽光充足且排水良好的土壤,pH值介於6到7.5之間。適當的陽光和無霜期對胡桃的生長和果實發育至關重要。樹木的授粉也對胡桃的質量和產量有益。
4.3 收穫胡桃
胡桃通常在秋季收穫,當胡桃成熟時。一旦外殼裂開,表示胡桃已經成熟,可以從樹上搖落或從地上收集。為確保優質的胡桃,必須及時收集、分類和儲存在適當的條件下。
4.4 商業生產
商業胡桃生產涉及果園管理,包括病蟲害防治、灌溉和施肥。現代栽培技術,如嫁接和選育,有助於開發具有良好特性(如較大的尺寸和較高的油脂含量)的改良胡桃品種。美國是全球最大的胡桃生產國,主要產區包括加利福尼亞州。
胡桃的營養價值
胡桃富含多種營養素,包括蛋白質、纖維、單元不飽和脂肪酸、抗氧化物和多種維生素和礦物質。每100克胡桃約含有约690卡路里能量。
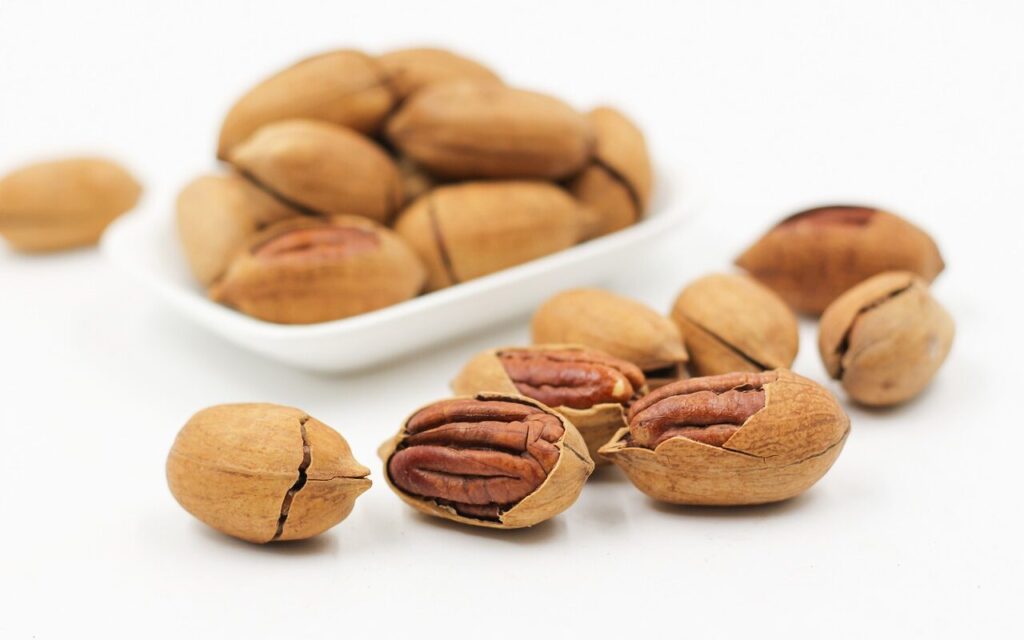

胡桃的健康益處
胡桃有許多健康益處,以下是其中幾點:
6.1 心臟健康
胡桃中的單元不飽和脂肪酸有助於降低壞膽固醇(LDL)和總膽固醇水平,從而降低心血管疾病的風險。
6.2 腦部健康
胡桃中的多種營養素,如抗氧化物、ω-3脂肪酸和維生素E,有助於保護腦部健康,減少老年癡呆症的風險。
6.3 消化健康
胡桃富含纖維,有助於促進腸道健康,預防便秘和其他消化問題。
6.4 重量管理
儘管胡桃富含營養,但適量食用可以幫助控制食慾,使人感到飽腹,有助於重量管理。
6.5 抗氧化特性
胡桃中的抗氧化物可以中和自由基,保護身體免受氧化損傷,有助於維持健康和抵抗慢性疾病。
胡桃在烹飪應用中的角色
胡桃在烹飪和烘焙中具有廣泛的應用。以下是一些例子:
7.1 烘焙
胡桃是許多烘焙食品的常見成分,例如胡桃派、胡桃餅乾和胡桃蛋糕。它們提供了獨特的口感和豐富的風味。
7.2 零食
胡桃可以作為美味的零食單獨食用。無論生吃還是烤過,都能帶來令人滿足的脆爽口感。
7.3 烹飪
胡桃可以添加到許多菜餚中,例如沙拉、炒飯和烤肉,為食物增添香氣和口感。
7.4 胡桃油
胡桃油是一種具有豐富風味的食用油,常用於調味、烹調和沙拉醬。
胡桃與節慶季節
在許多文化中,胡桃與特定的節慶季節相關聯。例如,在美國的感恩節,胡桃派是一道傳統的節慶食品,象徵著豐收和感恩的象徵。
胡桃在流行文化中的地位
胡桃在文學、電影和藝術作品中常常出現。它被視為智慧和豐富的象徵,在故事中扮演著重要角色。
可持續性和胡桃生產
胡桃生產需要耗費大量的水和土地資源。因此,可持續的胡桃生產和消費是至關重要的,包括節水灌溉方法和推動土地保護措施。
選購和儲存胡桃的小貼士
選購時,選擇外觀完整、無裂痕的胡桃,並注意是否有霉點或異味。儲存時,將胡桃置於密封的容器中,放在陰涼乾燥的地方或冷藏保存,以延長其保鮮期。

胡桃作為一種營養豐富且美味的堅果,在飲食和健康中扮演著重要角色。無論是作為獨立的零食還是烹飪的成分,胡桃都帶來獨特的風味和營養價值。了解胡桃的種植和生產過程,選購和儲存的技巧,以及胡桃的健康益處,有助於我們更好地享受這個美味的堅果。
是的,胡桃是良好的植物蛋白質來源之一。每100克胡桃約含有約15克的蛋白質,是素食者獲取蛋白質的良好選擇。
胡桃因其飽腹感和營養價值可以作為減肥計劃的一部分。其中的蛋白質、纖維和健康脂肪組合有助於控制食慾,防止過食。
如果儲存得當,胡桃可以保存數個月至一年。冷藏儲存可以延長其保鮮期。
是的,如果有足夠的空間和適當的生長條件,家庭花園也可以種植胡桃樹。
對於堅果過敏的人,食用胡桃可能會引起過敏反應。在這種情況下,應該避免食用胡桃或諮詢醫生的建議。
Contact Info:
Introduction on Pecans
Pecans, the delicious nuts with a distinctive flavor and crunchy texture, have captivated the taste buds of people around the world for centuries. From being a staple food source for Native American tribes to becoming an essential ingredient in various culinary creations, pecans have a rich historical and cultural significance. In this article, we will explore the world of pecans, uncover their nutritional benefits, delve into their cultivation and production, and discover their versatile applications in cooking and baking.
What are Pecans?
Pecans (Carya illinoinensis) are a species of hickory tree native to North America. The name “pecan” is derived from the Native American word “pakani,” meaning “nut that requires a stone to crack.” Pecans are characterized by their oval shape, smooth brown shells, and buttery, sweet taste. They are commonly used in desserts, such as pecan pie, and are also enjoyed as a snack on their own.
Historical Significance of Pecans
Pecans have a deep-rooted history in the United States, dating back thousands of years. Native American tribes, including the Apache, Cherokee, and Chickasaw, revered the pecan tree as a symbol of abundance and relied on its nuts as a valuable food source during harsh winters. Pecans also played a significant role in the diet of early European settlers and became a cherished ingredient in traditional Southern cuisine.
Cultivation and Production of Pecans
4.1 The Pecan Tree
Pecans are cultivated from the majestic pecan tree, which can reach heights of up to 150 feet. These deciduous trees thrive in warm climates, primarily in the southern regions of the United States, such as Texas, Georgia, and Louisiana. The pecan tree’s lifespan can extend over several generations, with some trees producing nuts for over a hundred years.
4.2 Growing Conditions
Pecan trees require specific growing conditions to flourish. They prefer deep, well-drained soils with a pH level between 6 and 7.5. Adequate sunlight and a frost-free growing season are crucial for optimal nut development. The trees also benefit from cross-pollination, as it enhances the quality and quantity of the pecan crop.
4.3 Harvesting Pecans
Pecans are typically harvested in the fall, when the nuts reach maturity. Once the outer husks split, indicating readiness, the nuts are shaken loose from the trees or collected from the ground. To ensure high-quality nuts, they must be promptly gathered, sorted, and stored under proper conditions.
4.4 Commercial Production
The commercial production of pecans involves orchard management, including pest control, irrigation, and fertilization. Modern cultivation techniques, such as grafting and selective breeding, have contributed to the development of improved pecan varieties with desirable characteristics, such as larger size and higher oil content. The United States is the leading producer of pecans, with the majority of the crop coming from the states of Georgia, Texas, and New Mexico.
Nutritional Value of Pecans
Pecans are not only a delectable treat but also a nutritious addition to a well-balanced diet. These nuts are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. A one-ounce (28-gram) serving of pecans provides approximately 196 calories, 3 grams of protein, 20 grams of fat, and 4 grams of carbohydrates. They are also an excellent source of dietary fiber and contain notable amounts of vitamins E and B, magnesium, zinc, and antioxidants.
Health Benefits of Pecans
Pecans offer an array of health benefits, making them a valuable inclusion in your diet. Let’s explore some of the advantages pecans offer:
6.1 Heart Health
Consuming pecans as part of a balanced diet may promote heart health. Pecans contain monounsaturated fats, such as oleic acid, which are beneficial for reducing LDL cholesterol levels and maintaining healthy blood pressure. They also contain antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and protect against cardiovascular diseases.
6.2 Brain Health
The vitamin E content in pecans plays a vital role in maintaining brain health. Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant and protects brain cells from oxidative stress, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s.
6.3 Digestive Health
The fiber content in pecans aids in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Fiber promotes regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and contributes to a balanced gut microbiome. It also supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
6.4 Weight Management
Despite their relatively high calorie content, pecans can still be a valuable addition to a weight management plan. The combination of protein, fiber, and healthy fats in pecans provides a feeling of fullness, which can help control appetite and prevent overeating.
6.5 Antioxidant Properties
Pecans are rich in antioxidants, including phenolic compounds and flavonoids. These antioxidants help protect the body against oxidative stress caused by free radicals, which can contribute to chronic diseases and cellular damage.
- Myth 1: Pecans are high in fat and should be avoided in a healthy diet. In reality, the fats in pecans are mostly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for overall health.
- Myth 2: Pecans are too calorie-dense to be included in a weight loss plan. When consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet, pecans can actually aid in weight management due to their satiating properties.
- Myth 3: Pecans are not suitable for individuals with nut allergies. While pecans are tree nuts, they are relatively low on the list of common allergens and may be tolerated by some individuals with nut allergies. However, caution should always be exercised, and medical advice should be sought if uncertain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pecans are not just a delicious nut; they are a versatile ingredient with a rich history and numerous health benefits. From their cultivation and production to their applications in cooking and baking, pecans have firmly established themselves as a beloved ingredient in various culinary traditions. So, whether you’re enjoying a slice of pecan pie during the holiday season or adding a handful of pecans to your favorite salad, savor the unique flavor and embrace the remarkable qualities that make pecans a true delight.











Leave a Reply